The WISC Test (Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children)
Updated November 20, 2023
- What Is the WISC?
- Key Features of the WISC Test
empty
empty
empty
empty
- Example Questions on the WISC Test
- The 10 Subtests on the Test
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
- WISC-V Age Bands
empty
empty
empty
- How to Prepare for the WISC
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
There are several assessment tools available to determine a child's intelligence, strengths and development areas.
One of the most popular and widely used tools in evaluating cognitive abilities is the Weschler Intelligence Scales.
What Is the WISC?
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC), or WISC V (updated from the previous WISC IV test), is a widely used psychological assessment tool originally developed by David Wechsler, a prominent psychologist.
The test measures the cognitive abilities and intelligence of children and adolescents aged six to 16 years.
The WISC is administered by a trained psychologist or qualified clinician and is used for a variety of purposes:
-
Assessing intellectual functioning – It provides a detailed evaluation of a child's cognitive abilities, including verbal and non-verbal reasoning, working memory, processing speed and perceptual reasoning.
-
Identifying learning disabilities – The WISC can help identify learning disabilities or cognitive impairments affecting a child's academic performance, such as ADHD, dyslexia or intellectual disabilities.
-
Educational planning – The results help educators tailor their teaching methods to meet the specific needs of each student.
The WISC V test lasts between 65 and 80 minutes and consists of subtests assessing different aspects of a child's cognitive abilities.
These subtests are designed to be age-appropriate and may involve tasks such as:
- Solving puzzles
- Answering questions
- Completing various cognitive tasks
The test method can be online or one-to-one, depending on the circumstances.
The scores obtained from the WISC are summarized using the WISC intelligence scale. This provides an overall IQ score used to measure a child's intellectual abilities.
WISC V scores can also provide insights into a child's strengths and weaknesses.
Prepare for the WISC Test with TestPrep-Online
Key Features of the WISC Test
There are several main features of the WISC test. These include:
Age-Appropriate Versions of the WISC V Test
The WISC test is available in versions tailored to different age groups. Each version considers the developmental changes that occur during childhood and adolescence.
Subtests of the WISC Test
The WISC test comprises several subtests. Each of these subtests assesses different cognitive abilities. These subtests cover:
- Verbal comprehension
- Perceptual reasoning
- Working memory
- Processing speed
Standardization of the WISC Test
The WISC is standardized using a large representative sample of children in the same age group.
This means a child's performance is compared to their peers in the same age range.
Standardization allows for interpreting a child's scores in the context of their age group.
Individualized Assessment
The WISC test allows for an individualized assessment of a child's cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
By evaluating a child's performance on different subtests and cognitive domains, clinicians can gain insights into areas where the child excels and areas that may require additional support.
All tests are administered by a trained psychologist, enabling personalized assessment if necessary. This also ensures that the scores are interpreted correctly.
Example Questions on the WISC Test
The specific questions and tasks on the WISC test vary between different versions of the WISC and are adapted based on the child's age and ability level.
For example, some questions aimed at younger children can be picture-based, where children point to the correct answer from those given.
Below are examples of questions or tasks that might be found on some of the subtests of the WISC.
1. What does the word 'transparent' mean?
2. In what way are a bicycle and a tricycle similar?
3. Four families go to the cinema together. Before going in to watch the movie, they order four pizzas at $9 each, three trays of nachos at $7.50 each, and eight drinks at $1.25 each. They want to split the bill equally.
How much does each family pay?
a) $17
b) $17.13
c) $16
d) $18.25
4.
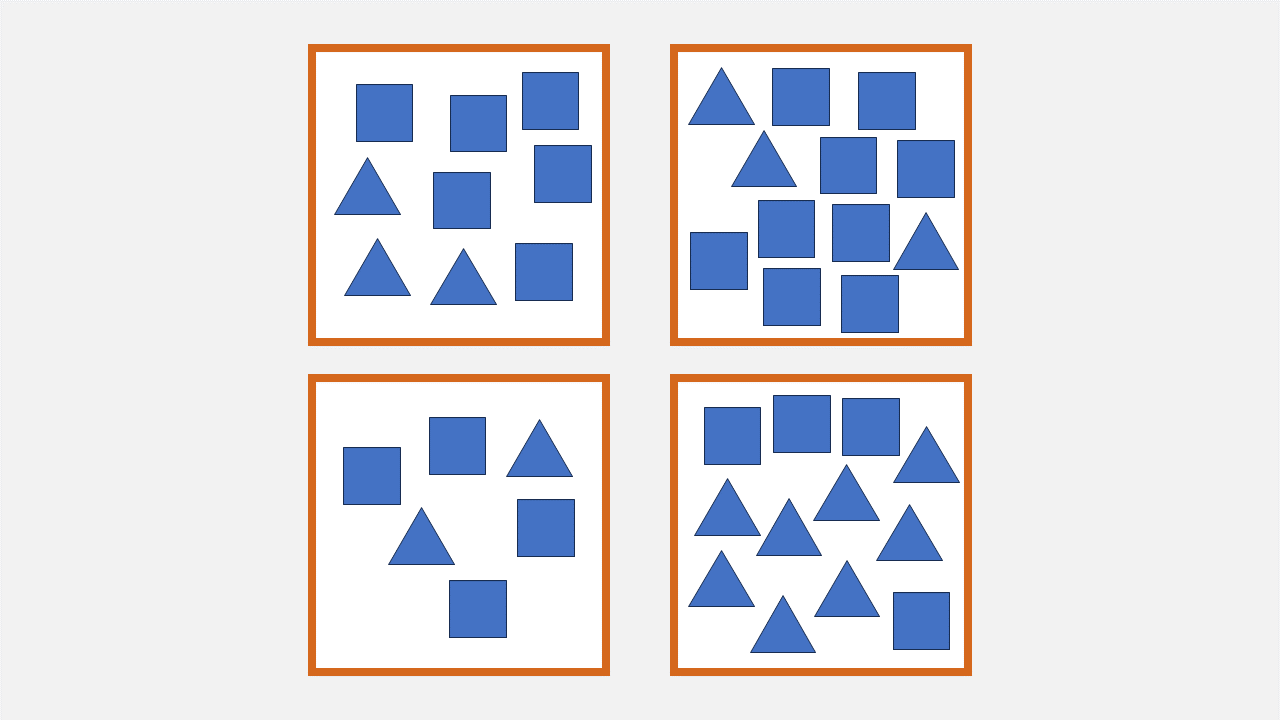
Which box has three times as many squares than triangles?
a) The box with six squares and three triangles
b) The box with three triangles and nine squares
c) The box with two triangles and four squares
d) The box with four squares and eight triangles

If you need to prepare for a number of different employment tests and want to outsmart the competition, choose a Premium Membership from JobTestPrep.
You will get access to three PrepPacks of your choice, from a database that covers all the major test providers and employers and tailored profession packs.
The 10 Subtests on the Test
Over the years, there have been multiple versions of the WISC, each with its subtests, norms and scoring procedures.
The most recent edition of the test is the WISC V test.
The WISC-V includes a revised set of subtests and updated norms. It is designed to provide a more accurate and comprehensive assessment of a child's cognitive abilities, including verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory and processing speed.
The WISC V test includes 10 primary subtests that contribute to calculating various composite scores, including the Full Scale IQ score.
The 10 subsets of the test include:
Verbal Comprehension – Similarities
This subtest of the WISC V test assesses a child's ability to recognize and understand relationships between words and ideas. It measures abstract verbal reasoning and verbal comprehension skills.
Verbal Comprehension – Vocabulary
Questions center around defining or explaining the meaning of specific words in this subtest. It assesses a child's vocabulary and verbal knowledge.
Visual Spatial – Block Design
Block Design evaluates non-verbal reasoning and visual-motor integration skills. Examples include replicating specific geometric patterns using colored blocks.
Fluid Reasoning – Matrix Reasoning
Matrix Reasoning assesses non-verbal reasoning abilities. The test taker is asked to identify a missing part in a visual pattern to complete it.
Fluid Reasoning – Figure Weights
This subtest measures a child's ability to understand and apply quantitative concepts. For example, they may have to visually compare and balance weights of different objects.
Working Memory – Digit Span
Digit Span assesses a child's working memory capacity. The child must repeat a series of digits in the order presented and then in reverse order.
Processing Speed – Coding
Coding evaluates a child's processing speed and fine motor skills. The child is required to match symbols to numbers as quickly as possible.
Visual Spatial – Visual Puzzles
Visual Puzzles assess a child's visual spatial reasoning abilities. The child must identify and choose the correct visual puzzle piece.
Working Memory – Picture Span
Picture Span measures a child's working memory for visual information. The test taker is shown a picture series and asked to repeat the sequence in the correct order.
Processing Speed – Symbol Search
Symbol Search assesses attention to detail and processing speed. Children must identify which target symbols match any of the symbols presented in a list.
WISC-V Age Bands
The WISC V test is used with children between the ages of six and 16 years. These age bands ensure that the WISC-V is administered to individuals within the appropriate developmental range, ensuring the results are accurate and used appropriately.
The WISC V Age Six to Seven Years (Primary Level Test)
The primary level of the WISC-V is designed for children aged six to seven years. This age group typically includes children in early elementary school and consists of all test subsets.
The WISC V Age Eight to 12 Years (Intermediate Level Test)
The intermediate level of the WISC-V is designed for children aged eight to 12 years, which corresponds to late childhood and early adolescence. In addition to the subtests included in the primary level, the intermediate level may also include:
- Visual puzzles – Assesses visual-spatial reasoning by having children complete visual puzzles
- Information – Evaluates general knowledge by asking questions about various age-appropriate topics
- Arithmetic – Measures mathematical reasoning and problem-solving abilities
The WISC V Test Age 13 to 16 Years (Adolescent Level Test)
The adolescent level of the WISC-V test is designed for individuals aged 13 to 16 years, covering early to mid-teens.
This level includes all the subtests from the primary and intermediate levels in addition to the following:
- Letter-number sequencing – Assesses working memory and recall
- Symbol search – Measures processing speed and attention to detail by having individuals match symbols to numbers
- Coding – Assesses processing speed and fine motor skills by matching symbols to numbers
How to Prepare for the WISC
Unlike traditional exams, the WISC is designed to assess a child's inherent cognitive abilities and is not meant to be studied for like an exam.
However, some important steps can be taken to ensure the individual taking the WISC assessment feels confident in sitting the test.
Step 1. Familiarity with the testing environment
If the test is being taken as a one-to-one test, and if possible, visit the testing location in advance. This is so the child feels more comfortable on the test day. Knowing where they will be and what the room looks like can help reduce anxiety.
Step 2. Stay calm and positive
Maintain a positive attitude and reassure the child that the WISC V test is an opportunity to show people what they know and can do.
Step 3. Emphasize rest and health
In the weeks leading up to the test, ensure the test taker gets enough sleep, eats well and stays physically active.
Step 4. Practice tests
Encourage the test taker to follow the instructions, read each question or task carefully and take their time. Remind them that asking for clarification is okay if they need help understanding something. It’s also a good idea to practice some WISC V sample questions to get used to the format.
Step 5. Review subjects
Ensure that the subject subsets are covered when practicing. This ensures familiarity with the concepts used in the test. This means the test taker can perform to the best of their natural abilities in the test.
Step 6. Talk about the test positively
Explain that the test is an opportunity to learn more about their strengths and abilities, and it can help teachers and parents provide support in areas where they may need it.
Step 7. Practice relaxation techniques
Teach the test taker some relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or visualization, to use if they feel anxious during the test.
The WISC V test is a standardized psychological assessment tool to measure children's and teens' cognitive abilities and intelligence. It includes a series of subtests to evaluate verbal and non-verbal reasoning, working memory and processing speed, providing insights into a child's cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
The WISC assesses cognitive abilities and intelligence. It helps in educational planning, identifying learning disabilities and understanding intellectual functioning. The test measures verbal and non-verbal reasoning, working memory and processing speed.
The WISC V is designed to assess a child's cognitive abilities and intelligence. There isn't a pass or fail mark. The results provide insights into a child's cognitive strengths and areas where they may need additional educational support or intervention.
Preparation for the WISC V test includes maintaining good physical and mental health. Participating in activities stimulating cognitive development, such as reading and solving puzzles, is also helpful. The test taker can take practice tests of the subsets in the overall test. WISC V sample questions are included in this article.
A "gifted" score on the WISC test refers to a Full Scale IQ score that falls significantly above the average range. A Wechsler intelligence scale score above 130 is often considered gifted. Scores above 145 to 159 indicate an individual as being highly gifted. Those scoring above a score of 160 on the Wechsler intelligence scale are considered to be extremely gifted.
The WISC V test measures a child's inherent cognitive abilities and intelligence. It assesses verbal and non-verbal reasoning, working memory and processing speed. The WISC assessment provides insights into a child's intellectual strengths and weaknesses.
Each WISC V test subset typically comprises 10 to 20 questions. This can vary depending on the version of the test administered and the age banding of the WISC V test.
Final Thoughts
The WISC test evaluates the cognitive abilities and intelligence of children and adolescents aged between six and 16 years of age. The test comprises several subtests measuring verbal and non-verbal reasoning, working memory and processing speed.
The WISC V serves several purposes. It helps diagnose learning disabilities and cognitive impairments, assisting educators in tailoring educational strategies and interventions. It also offers insights into a child's cognitive strengths and weaknesses, facilitating individualized educational plans.
While the Wechsler intelligence test evaluates an individual's natural abilities, preparing for the test by taking care of well-being, practicing questions and creating strategies to keep calm is advised before taking the test.



